|
The
Carpathian language of today is essentially identical to the Carpathian
language of thousands of years ago. A "dead" language
like Latin has evolved into a significantly different modern language
(Italian) because of countless generations of speakers and great
historical fluctuations. In contrast, many of the speakers of
Carpathian from thousands of years ago are still alive. Their
presence -- coupled with the deliberate isolation of the Carpathians
from the other major forces of change in the world -- has acted
(and continues to act) as a stabilizing force that has preserved
the language over the centuries. Carpathian culture has also acted
as a stabilizing force. For instance, the Ritual
Words, various healing chants (including The
Lesser Healing Chant and The
Great Healing Chant, and other cultural artifacts have
been passed down the centuries with great fidelity.
One small
exception should be noted: the splintering of the Carpathians
into separate geographic regions has led to some minor dialectization.
However the telepathic links among all Carpathians has ensured
that the differences among dialects are relatively superficial
(e.g., small numbers of new words, minor differences in pronunciation,
etc.), since the deeper, internal language of mind-forms has remained
the same because of continuous use across space and time.
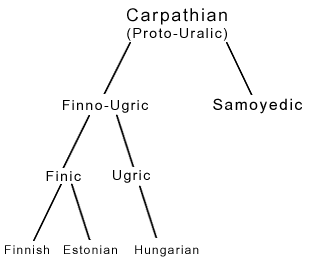
The Carpathian
language was (and still is) the proto-language for the
Uralic (or Finno-Ugrian) family of languages. Today, the Uralic
languages are spoken in northern, eastern and central Europe
and in Siberia. More than 23 million people in the world speak
languages that can trace their ancestry to Carpathian. Magyar
or Hungarian (about 14 million speakers), Finnish (about 5 million
speakers), and Estonian (about 1 million speakers), are the
three major contemporary descendents of this proto-language.
The only factor that unites the more than twenty languages in
the Uralic family is that their ancestry can be traced back
to a common proto-language -- Carpathian -- which split (starting
some 6,000 years ago) into the various languages in the Uralic
family. In the same way, European languages such as English
and French, belong to the better-known Indo-European family
and also evolve from a common proto-language ancestor (a different
one from Carpathian).
|